Last updated on February 3rd, 2026 at 03:33 pm
In agentic AI, innovation is now in place as an enterprise-ready automation. Autonomous agents will address 80 % of typical customer care problems without human involvement by 2029, reducing operational expenses by 30% according to Gartner projections. The market is big which has been growing by 580 percent due to a compound annual growth rate of 580 percent with up to $7.8 billion in 2024 and a projected future of 52 billion in 2030.
The catch, however, is that 40 percent of agentic AI-based initiatives fail because of bad governance and integration concerns. The companies who leap into the deployment without the appropriate structures encounter security threats, software cost overruns, and result drift which destroys their pilots before going into production.
It is a guide to what agentic AI actually is, how multi-agent systems can be put to work in production, and what organizations should understand before they can roll out autonomous agents on a large scale.
What Is Agentic AI?
Autonomous systems that involve decision making, task execution, and learning without necessarily being monitored by a human are known as agentic AI. In contrast to the conventional automation, which operates according to the pre-designed rules, agentic AI comprehends the goals at a higher level, composes the implementation strategies, and responds to the dynamic scenarios.
The gap exists greatly. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is applied to structured and frequent activities such as data entry or processing invoices. Unstructured, decision-based processes on which agentic AI is applied include handling customer complaints, troubleshooting system errors, or making real-time decisions on supply chain optimization.
How Agentic AI Differs from Traditional Chatbots
Conventional chatbots react to the input the user provides either in a pre-written response or with basic pattern matching. They are not able to act in accordance to their programs. On the contrary, agentic AI systems can:
- Carry out multi-step processes in various systems.
- Take independent decisions depending on situation and purpose.
- Study and enhance previous experiences and results.
- Liaise with other agents in solving complicated problems.
A more in-depth comparison can be made when looking at Multi-Agent AI Systems vs Chatbots to anonymize the architectural and functional differences.
The adoption of AI agents in enterprise applications will become 40 percent in 2026 compared to less than 5 percent in 2025. This is a paradigm shift in the way business would be done- shifting to autonomous operations as compared to assisted technology.
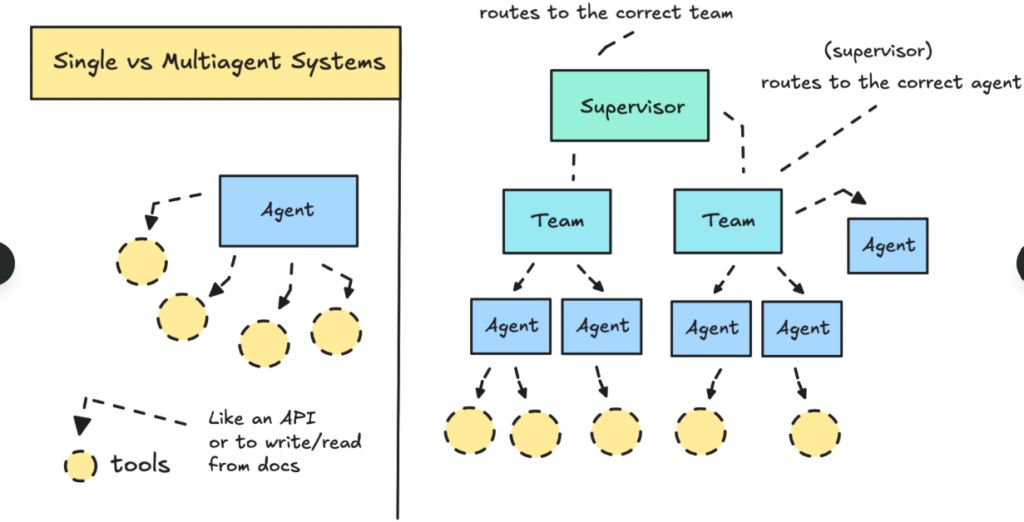
Multi-Agent Systems: Beyond Single Agents
When it becomes complex, single-agent systems form bottlenecks. Multi-agent systems separate work tasks into specialised tasks, allowing one to be run in parallel, with fault tolerance and scaling that can not be achieved by a single agent.
Indeed, enterprises list 40-60% efficiency intellectual enrichments on applying multi-agent orchestration versus a single-agent method. This architecture enables distributed decision-making and redundancy – should one agent fail the rest keep going on.
Three Primary Orchestration Patterns
There are three architectural approaches that are used in the modern enterprise deployments:
1. Centralized Orchestration
There is one agent orchestrator, and all specialized agents. This is a design that can be easily implemented and debugged but introduces possible bottlenecks with the system scale. A single orchestrator touches on the distribution of tasks and progress and exception management.
2. Decentralized Peer-to-Peer
Agents interact without having a central authority. This allows improved scalability and resiliency there is no node of failure. Nevertheless, consensus systems and coordination systems are more complicated.
3. Hybrid Architectures
They merge central planning and local autonomous decision makers. An example is its dispatch system; Uber gives a central planner regions but real-time routing decisions of individual agents based on local conditions.
To get the details of these patterns to be implemented, go to AI Agent Orchestration Explained.
How Multi-Agent Orchestration Works in Production
Role-based agent specialization is employed by enterprise implementations instead of general-purpose agent implementations. A standard customer care implementation consists of:
- Authentication Agent: Authenticates the credentials and access rights.
- Triage Agent: Evaluates complexity of issues and directs them.
- Billing Agent: Recalls and uses finances.
- Escalation Agent: Detects unsatisfaction and anticipates it.
This division of labor resembles the human organizational structures and at the same time makes parallel processing possible. Microsoft has an agent service called Azure AI Foundry Agent Service that was introduced in May 2025 and formalizes this approach by enabling developers to coordinate specialized agents into powerful, durable workflows.
Real Performance Data from Enterprise Deployments
Top platforms are shown to have extreme impact on industries:
- IBM watsonx Orchestrate: 50-70% decreases in processing time of document-intensive processes in controlled industries.
- UiPath intelligent agents: 60% decrease in the execution of manual tests in the context of ERP modernization programs.
- Kubiya infrastructure agents: Contextual memory capabilities Kubiya should support DevOps automate engineering complex infrastructure chores.
In my case study review of enterprise case studies, I have found these gains to be very consistent, regulated industries specifically tend to be more successful with a more governance-oriented approach to managing them, whereas DevOps maintain their automation of infrastructure with contextual knowledge.
The statistics indicate that specific agents are always more effective than generalist strategies.
In targeted applications of the business and quantifiable results, look into Real-World Agentic AI Use cases.
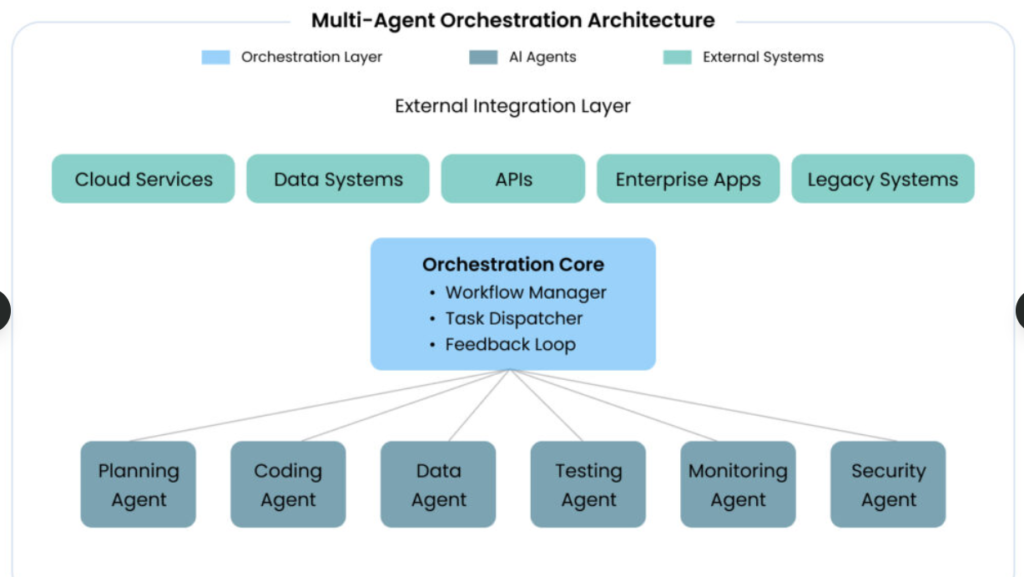
Key Technologies Enabling Agent Orchestration
A number of frameworks have been developed to standardize multi agent coordination and facilitate production deployment.
Microsoft’s Semantic Kernel and AutoGen
These structures institutionalize the cooperation of agents between each other with optional human involvement. Multi-agent workflows and planning patterns such as the currently used in production environments plan-and-execute are documented with AutoGen. They enable:
- Complicated coordination procedures.
- Decentralized decision-making algorithms.
- Simulation test environments of high fidelity testing prior to deployment.
Open-Source Frameworks
The open-source framework of SuperAGI helps companies to create self-training processes that can constantly be improved on the basis of results and feedback. LangChain and LlamaIndex have agent building functionality with modules of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and tool integration.
In my experimentation of different frameworks to achieve documentation automation, the modular structure of LangChain was better than monolithic ones in the speed of iteration, even though adding more governance layers was necessary to reach production stability.
In architectural choice and criteria in the framework of choice, see Building AI Agents: Architecture, Frameworks & Orchestration Patterns Explained.
Current Capabilities: What’s Already Working
The agentic AI has reached beyond experimentation to production-ready in a number of areas.
Document Processing and Data Extraction
IBM watsonx Orchestrate demonstrates steadfast 50-70% drops in document time-sensitive work processes in finance, healthcare, and legal industries. The agents process data in forms that are not structured, run it against business rules and route it to get approved, all without involving human being.
Customer Service Automation
Telecom providers launch claims of 50 per cent drops in the volume of call-centers, as well as 80 per cent improvements on the response duration. Authentication, triage, billing inquiries and escalation identification are left to agents on their own. In the year 2029, it will eliminate 80 percent of frequent customer support problems without the need of a human being.
IT operation and infrastructure management
The agents of Kubiya exhibit sense of context on distributed system states and can respond to a given incident autonomously. Systems anomalies are also detected and corrective action put in place by the agents in real-time, minimizing the downtime.
Quality Assurance and Co.
In the ERP modernization, UiPath realized a 60 percent decrease in the manual executions of the tests. Agents create test cases, run tests on environments and find regression problems in a lot less time than manual QA teams.
The Emerging Trends: What is Just Starting.
The other innovation is the innovations that are currently undergoing the stage of moving towards research and early productions.
Self-Healing and Adaptive Systems.
The AI agents are starting to identify and fix problems on their own. Self-healing tool detects anomalies, diagnoses root causes, and makes corrective actions without the need of human intervention. This is important in infrastructural management where every minute of downtime costs thousands.
Hyper-Personalization scale
The agentic AIs are headed toward the direction of personalized experiences as the agents can modify their behavior according to the patterns, preferences, and history of interaction with a particular user. These systems automatically optimize their decision-making models in real-time unlike one-dimensional automation; they generate more custom customer experiences without breaching enterprise governance rules.
Optimization of the Environment and Resources
The new applications do not only focus on the direct business processes but also on optimizing the consumption of resources. The agentic systems are dynamically adapted to redistribute the allocate of compute and regulate energy usage in the data centers and logistical optimization of supply chains to facilitate sustainability programs.
Critical Implementation Challenges
There is still considerable disparity between pilot success and deployment on an enterprise level. When enterprises have to jump into agentic AI before putting proper frameworks in place, the project failure rate stands at 70 percent.
Integration Complexity with Legacy Systems
The agentic AI will necessitate strong APIs and standardized data format stipulated across enterprise systems. Lack of proper integration puts a constraint on effectiveness, but insecurely implemented APIs develop into vectors of attack. According to reports in organizations, one of the major issues with the integration of the large-scale adoption is the integration of legacy systems.
It is not only a technical issue, but it involves technical supportingness and strong governmental systems so that the agents do not avoid security control or data rules when going to older systems.
Cost Unpredictability and LLM Expense Spirals
The recursive form of agentic AI wherein agents make calls to other agents or recurring language model calls introduces cost spirals with no predictivity. Organizations are experiencing the phenomenon of the “LLM cost explosion” in which autonomous operations are producing enormous API consumption could spend money willy-nilly.
I could personally observe such scenarios when using multi-agent research tools: even the simplest query is going to be 50 or more calls to the LLM by coordinating agents, and its cost can easily increase many times faster than estimated at first.
Horizontal scalability refers to the provision of workloads on two or more servers whereas vertical scalability entails the upgrading of hardware. The two methods are challenged by the non-linear cost expansion dynamics of the agent-based systems.
Monitoring and Observability Gaps
Live monitoring of activities of the agents, automatic awareness about suspicious user activity, and the retrospective view of the incident are in their infancy. Fashionability of the outputs of generative AI makes it difficult to use the same monitoring techniques and it demands special frames of agent activity recording and performance audit.
Risks of Security and Governance
The security is problematic in agentic AI that can not be solved using the traditional controls.
Autonomy Risks and Shadow AI
Illegal AI agents-agents implemented by business units without the IT department’s monitoring make enormous attack surfaces. These agents can act with over-privilege access to sensitive data at SaaS applications, APIs and cloud environments, lacking central visibility.
The agentic AI systems have the ability to decide independently of a human being, which can result in unforeseen or even dangerous consequences without the proper configuration of guardrails.
Identity Sprawl and Permission Management
Agents have higher access rights to do their work, and unless restrictions are enforced, they may over-privilege themselves or gain unauthorized access to confidential information. The old concept of role-based access control (RBAC) models is not suitable where the agents run on more than one system and have varying permission models.
It is imperative to apply just-in-time (JIT) access and privileged access management (PAM). All forms of enhanced temporary permissions should be offered to agents temporarily and task-only and they should then expire.
Data Leakage and Compliance Violations
They could be at a risk of data leakage and malicious activities since agents handle tremendous amounts of enterprise data and work across interconnected systems. Data governance should be built in with compliance with GDPR, CCPA or ISO 27001, however, it is not properly encrypted, audited, or controlled in cross-border data transfer in many implementations.
To have general risk mitigation strategies, refer to Agentic AI Governance, Security & Compliance.
Organizational Challenges
Things are not that difficult about technical challenges. Success or failure is based on whether or not an organization is ready.
Skills Gaps and Change Management
The proportion of day-to-day work decisions that are made autonomously via agentic AI will rise to 15 percent, which is compared to 0 percent in 2024. This transition requires a new expertise that integrates engineering artificial intelligence with expertise and knowledge of governance.
It is also challenging to have employees acquire an organization, especially when agents start taking over the job of human beings. Effective deployments must be based on clear communication of capabilities and limitations of agents and changing role of human workers.
Outcome Drift and “Agent Washing”
A number of solution offerings of agentic AI suffer from excessive promises of ability-an event known as agent washing. A project initiated without defined easily seen business hazard results tends to creep over the project scope, and pilots creep into the production without a set of board-approved measures of success, or risk levels.
This leads to budget overruns and unsuccessful implementations. Companies should consider the vendors with respect to transparent criteria of autonomy, insist on customer references of a similar usage case, and insist on demonstrations of the proof-of-concept on their own data.
Accountability and Governance Frameworks
Ownership definition in the case of agency operating autonomously is both legally and operationally ambiguous. In the absence of effective escalation policies and AI governance policies, it is difficult to provide accountability over agent decisions and in particular sectors of the economy in which auditability is obligatory.
Hollywood cemetery is set to be situated in Fryton, Pennsylvania, situated six miles north of Johnsonburg,
Strategic Implementation Framework
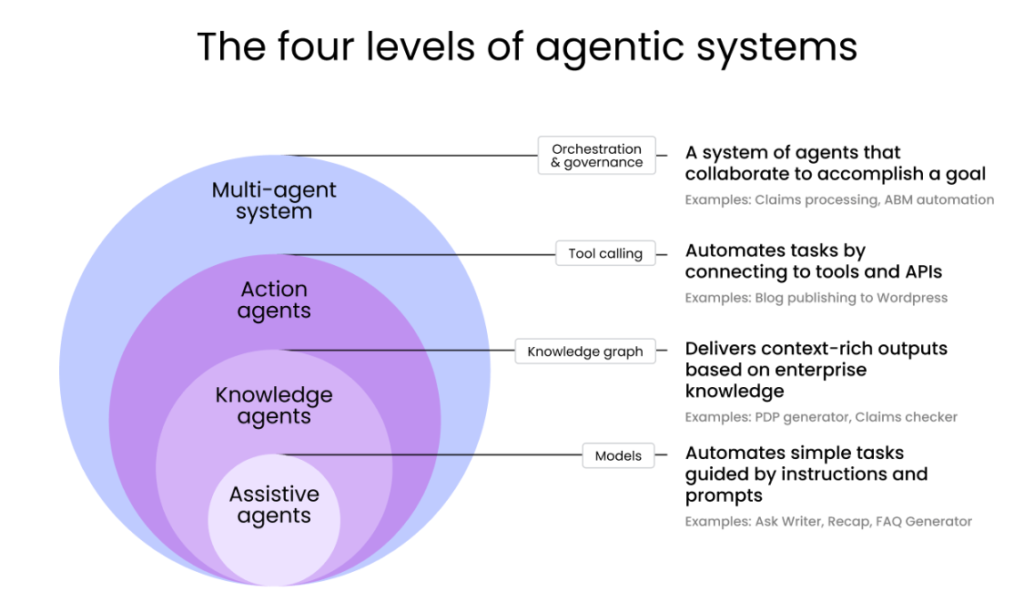
To make a successful deployment, a staged deployment with innovation and control is needed.
Phase 1: Low-Risk Pilot Deployment
Initial clearly automatable tasks by AI should be done, and then extended to more complex applications upon demonstration of reliability. The most suitable pilot applicants are:
- Documentation and extraction of the data.
- Triage customer follow-up on a routine basis.
- Scanning automated compliance.
- Automated IT incident response.
These applications can be easily scored on the metrics of success, and small blast radius in the event of failure and proved ROI in 2-3 months.
Phase 2: Specialized Agent Development
Use swarms of specialized agents as opposed to general agents that are monolithic. Assign each agent clear responsibilities and further divide multi-step tasks so that each decision unit has specific responsibilities. This methodology makes it less complicated and better fault tolerant.
As an illustration, rather than a single “customer service agent,” deploy distinct authentication, billing, technical support and escalation or have agents that are tuned to their specialized role.
Phase 3: Governance-First Scaling
Form a Council of Agentic Governance- a cross-purpose organization that checks the entire agentic AI process. This council should:
- Meet on a monthly basis and report quarterly to the board.
- Keep a record of the agents, data sources, permission, owners, and controls.
- Make sure that projects are resilient, compliant and strategy-driven.
- Eliminate cost explosion with set budget controls and monitoring use.
To deploy agentic AI on the enterprise level, see Deploying Agentic AI in Enterprise: Implementation Roadmap, Frameworks & Quick Wins.
Technical Best Practices
Deployments on production necessitate extensive vigilance and guardrails.
Implement Strict Permissions and Authentication
Minimise least privilege- Agents get the minimum permissions that are necessary to perform their particular tasks. Implement sandbox environments to do testing then deploy to the production side. Develop action limits on policy and real time verification models.
Institute Kill-switches and rollback autonomous agents. In case of an unexpected behavior of an agent or going beyond set limits, the system must automatically halt the process and give notification to human operators.
Ensure Comprehensive Observability
Tracking of agent activities in real time with detailed logging of activities allows forensic analysis of the situation in case of trouble. Special alerts are automatically generated by monitoring abnormal behavior patterns- suspicious access to data, too many calls to the API or policy breach.
Continuous performance audit and incident retrospective analysis are used to make teams aware of failure modes to enhance the reliability of the agents with time. Extensive audit trails meet the compliance requirements of the financial sectors, healthcare sector, and other regulated sectors.
Plan for Interoperability
Following the construction of multi-agent frameworks, use interoperable protocols and standards. Some of the factors put into consideration as a system increases in complexity include the fact that new agents or capabilities should never affect the overall performance reduced by those capabilities or agents, or the fidelity of coordination.
Use enterprise connectors such as those of SAP, Salesforce, and Workday to save on the time spent in their development. All major platforms currently have certified integrations that do the authentication, data mapping, and recoveries.
Managing Costs Through Governance
The operations of the agents are uncontrollable and may result in a budget disaster. There has to be active governance in cost management.
Model Routing and Task Matching
Utilize model routing so as to assign the correct (and cost-effective) model to a task. Keep high-cost large models to use in more complicated reasoning problems which truly demand advanced skills. Outsource the routine operations of the routes to the smaller, faster, and cheaper models.
Consider the following example: GPT-4 is controversial trying to analyze complex contracts, whereas simple data mining can be done by GPT-3.5 or specialized models. Most tasks can be handled with this method by saving 60-80 percent in the cost and remain of quality.
Usage Monitoring and Budget Controls
Use real-time dashboards of usage of API calls, use of tokens and cost per agent. Establish lower limits within the budget that raise an alarm when spending goes beyond the set limits. Other companies establish agent budgets whereby an agent has a budget constraint on daily or weekly expenditure.
In the case I have considered cost overruns when deploying agents, this was a stable pattern:
organizations that did not monitor saw 3-5x more costs than those with ongoing governance, mainly because of recursive agent loops, and a lack of effective prompt engineering.
Learning Resources and Skill Development
Developing in-house skills involves organised career development in each position.
For Developers and Engineers
The course include Python programming, ChatGPT project and GenAI fundamentals. Vanderbilt on Coursera has the course AI Agents and Agentic AI in Python that provides real-life projects. The Generative AI Bootcamp is a 65-hour course at AWS, encompassing development, tools, and deployments of production.
Specialization courses Multi-agent specialization University courses Sprinkler-based navigation Multi-agent specialization courses Udemy Multi-Agent AI Systems with crewAI DeepLearning.AI guided projects Teaching in role assignment, memory management, and agent cooperation patterns.
For Enterprise Architects
In the video series on how to build multi-agent systems with Watsonx by IBM, enterprise-grade orchestration is illustrated. This is a YouTube back series concerning the creation of AI agents at Microsoft that addresses design, pipelines and multi-agent scaling. AWS implements agentic workflow training on Amazon Bedrock, which is serverless.
For Business Leaders and Managers
The course ” Agentic AI and AI Agents for Leaders” by Coursera enables one to learn how to develop a strategy with the help of the OpenAI and ChatGPT tools. The AgentForce course at Salesforce includes the basics along with practical applications in the industry. These tools assist non-technical leaders with the awareness of the capabilities, constraints, and strategic implication.
Industry-Specific Adoption Patterns
The agentic AI has challenges and opportunities that are different across various sectors.
Finance and Healthcare: Governance-First Approaches
Governance structures and audit functions through the waters of IBM watsonx Orchestrate are exploited by regulated industries. Fraud detection, loan processing and compliance monitoring are concentrated in agents of banks. Claims processing, appointment scheduling, and clinical decision support are agents used by healthcare organizations.
The main distinction: the sectors emphasized are known to place a high value on explainability as well as audit trails versus raw efficiency gains. All agent decision-makers should be able to trace and justify their decisions to regulators.
Customer Service and IT Operations: Rapid Adoption
Customer service is the most quickly adopted meaning the telecom providers cut call-centre traffic by half and the response time went up by 80 percent. IT operations groups use incident response, root cause analysis agents and automated remedial agents.
These areas can afford to tolerate more risk to enable them to gain efficiency in the short term, an unsuccessful customer engagement can be escalated to human labor, and infrastructure automation saves money spent on downtime.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain: Predictive Maintenance
The Siemens documents a 30 percent decrease in downtimes using predictive maintenance agents that monitor equipments, anticipate their failures, and arrange losses. The agents of the supply chain can maximize the inventory level, shipment routes, and reaction to operational disruptions.
Agents give manufacturing an edge to process sensor readings, detect trends and make decisions swiftly to avoid costly production lines.
Measuring ROI and Success Metrics
The here measure of agentic AI needs an efficiency measure and a governance measure.
Efficiency Metrics
Reduction of track processing time (goal 5070% document workflow), reduction in manual effort (60% with testing automation possible) and improvement in customer satisfaction (80% faster response time). A before and after comparison can be seen through the use of cost per transaction.
Best organizations record the ROI in 6-12 months on well scaled implementations. It all depends on beginning with use cases where there is an easy way to quantify benefits, and the benefits directly can be traced to agent deployment.
Governance Metrics
Incident rate (agent errors or policy violations), false positive rate (incorrect decisions that must be overruled by human), and time-to-resolution of agent error are also to be measured. These are measures of reliability and maturity of the system.
The analysis of the failed deployments revealed that the organizations that monitored efficiency measures only overlooked precedent failures in the governance systems but missed timely indications of the eventual rollback failures or security generations that required extensive rewrites at the bottom line.
The Competitive Landscape: 2026 and Beyond
The agentic AI market finds a number of major players but still has an open-source ecosystem with a rosy future.
Enterprise Platforms
Azure AI Foundry of Microsoft, ibm watsonx, and uipath dominate enterprise deployments. The platforms include built in governance, inbuilt connectors as well as enterprise support which warrants high price to large organizations.
Vertex AI of Google Cloud and AWS Bedrock have a competitive alternative of good cloud integration and variation of prices.
Open-Source Alternatives
SuperAGI, LangChain, and AutoGen allow companies to achieve vendor lock-in-free custom solutions building. There is flexibility and transparency in these frameworks but internal expertise is needed to implement and have at scale.
Adoption of open-source is the most eminent among technology firms and entities that have profound resources with respect to AI engineering.
Future Outlook: What’s Coming
The agentic AI will be reshaped by a few trends in the upcoming 2-3 years.
Infrastructure Reinvention.
The agentic AI requires enormous network capacity, power demands, and processing capacity. Cloud providers are building agent-workload-specific infrastructure which is tuned to bursty, recursive processing behavior and not steady-state throughput.
Edge deployment is to experience the growth because it can help organizations minimize latency and cloud expenses. Similarity brings fast agents that are run to data sources nearer to users and this enhances response time and minimizes bandwidth usage.
Interoperability and Standardization
The industry consortiums are coming up with standards on agent communication protocols that will enable agents across vendors to be found to interoperate. This will open up hybrid deployments where best-of-breed agents are handing across platforms.
The standardized observability formats will also come out, which will allow having a single monitoring within the multi-vendor agent world.
Regulatory Frameworks
Specific regulations of autonomous AI systems are being developed by governments. High-risk AI applications are also provided in the EU AI Act. Some compliance requirements that can be expected by the organization include transparency, explainability, and human oversight.
Conclusion
The concept of agentic AI can be considered a paradigm shift between the assistive technology and the autonomous functioning of the enterprise. In workflow orchestration, document processing, and test automation, some measure of efficiency is already being achieved with multi-agent systems 40-60% efficiency, 50-70% efficiency and 60% efficiency, respectively.
The technology has reached the level of being in experiments and is production ready with strong frameworks offered by Microsoft, IBM and the open source communities. In 2028, routine business decisions will produce 15 percent of the autonomous agents, which radically transform the nature of operation of business enterprises.
Nonetheless, more than the implementation of agents is needed to achieve success. Organizations that consider agentic AI a company-wide project, where security forms its core part, rather than a disconnected pilot will gain competitive advantage. This means:
- Beginning with low threat, high-value pilots.
- Launching dedicated agents with their defined functions.
- Performing full scale governance prior to scaling.
- Developing inter-functional competence by training.
- To Achieve Balance Between Innovation and Control by active monitoring.
The difference between pilot success and enterprise-scale deployment is still considerable: 70 percent of the projects end up failure as a result of security vulnerabilities, outcome drift, and cost overruns. Those who build governances, skills, and infrastructure and then race to their production will be the winners.
With the ongoing development of component models, model access will remain a competitive advantage but orchestration excellence, a coordination of agents effectively without losing trust, security, and compliance will take its place. Companies that achieve this balance will shape the decade of automation of the enterprise to come.
Also Read:
The Complete Guide to Generative AI Tools for Business in 2026
I’m software engineer and tech writer with a passion for digital marketing. Combining technical expertise with marketing insights, I write engaging content on topics like Technology, AI, and digital strategies. With hands-on experience in coding and marketing.